Learning directions vocabulary in English helps us talk about movement, position, and location clearly and correctly. These terms are useful in real-life situations like asking for directions, traveling, giving instructions, reading signs, and using GPS systems. In this blog post, you will learn essential direction words in English with picture-based intent, categorized explanations, and simple examples. Understanding these words helps learners become more confident while speaking or understanding location-related conversations.
Want to learn more real-life vocabulary with visuals? Visit our Picture Vocabulary section to explore more topics through images and illustrations.
In This Page
Directions Vocabulary in English
Direction words describe where something is located, where it is going, or how to move from one place to another. These terms are used every day in transportation, education, public places, maps, and instructions. English learners should know how to use these words correctly to speak with clarity and avoid confusion. We will divide these terms into logical categories to make learning easier and faster.
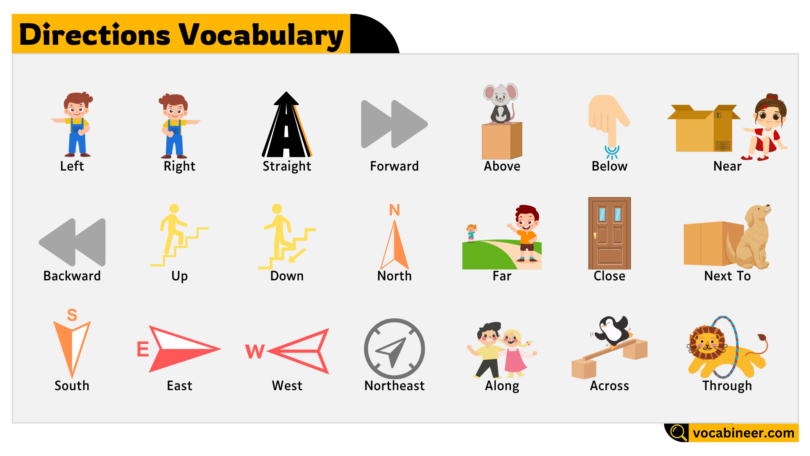
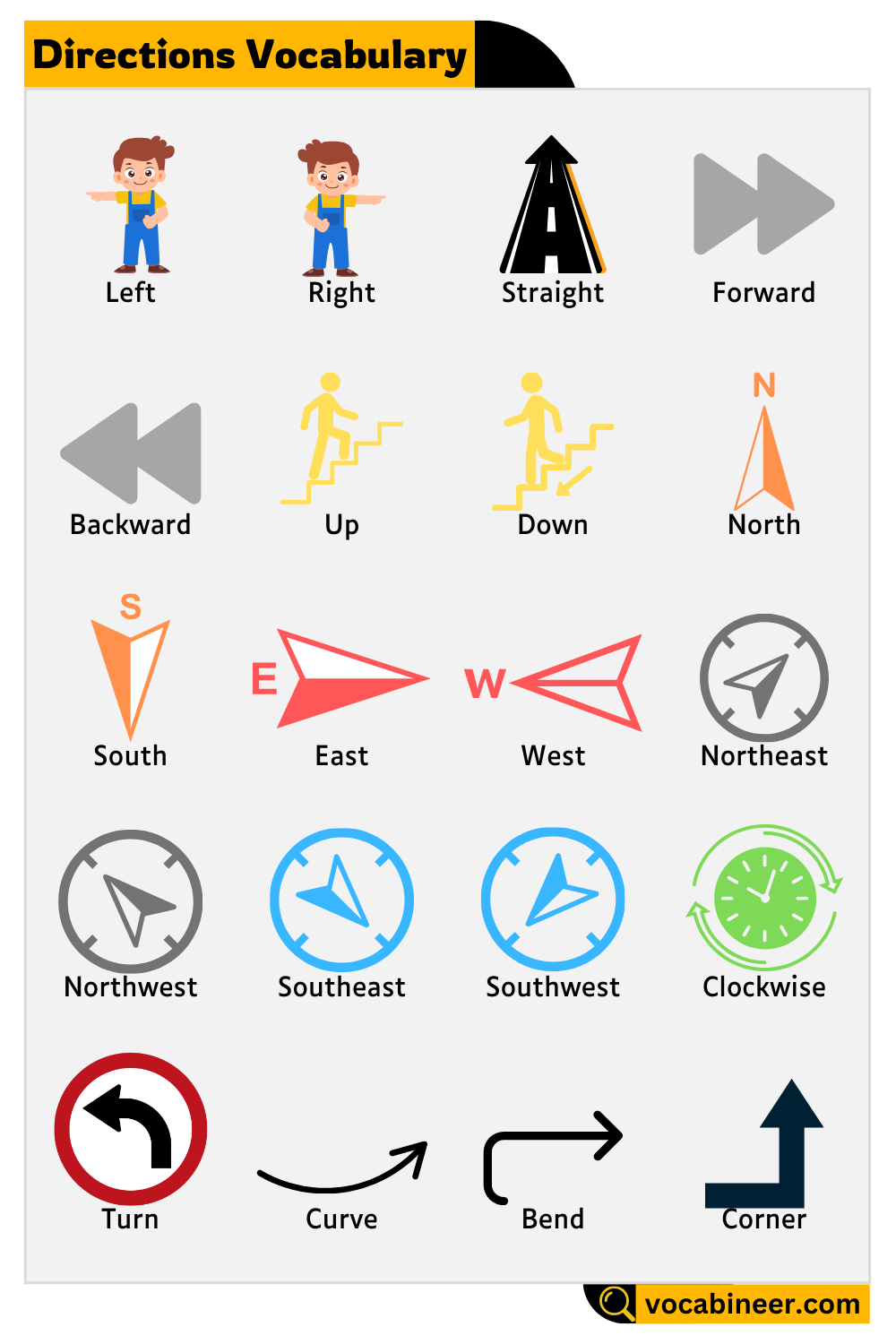
Basic Directions
These words describe general directions and are most commonly used in daily conversations, maps, and signs.
Left
Move or turn to the left side. Example: Ayesha turned left at the traffic light near the bakery.
Right
Move or turn to the right side. Example: Bilal’s house is on the right, just after the mosque.
Straight
To go in a direct line without turning. Example: Go straight for two blocks until you reach the library.
Forward
Move in the direction you’re facing, usually ahead. Example: Walk forward past the shop to get to the school gate.
Backward
Move in the opposite direction from where you’re facing. Example: He stepped backward to avoid getting hit by the swing.
Up
Direction towards a higher place or level. Example: The birds flew up into the sky after hearing the noise.
Down
Direction towards a lower place. Example: The keys fell down into the drain.
Cardinal and Intercardinal Directions
These are used on maps, compasses, and to describe geographical or large-scale directions. Useful in navigation and travel.
North
Direction pointing upward on most maps. Example: The school is north of the mosque.
South
Direction pointing downward on maps. Example: Head south to reach the market.
East
Direction to the right side of a map. Example: The sun rises in the east.
West
Direction to the left side of a map. Example: The sunset is seen in the west.
Northeast
Between north and east. Example: The station is northeast of the stadium.
Northwest
Between north and west. Example: Her house is located in the northwest corner.
Southeast
Between south and east. Example: Travel southeast to reach the garden.
Southwest
Between south and west. Example: The park is in the southwest area of the city.
Turning and Road Movement
These words describe specific movements or patterns when navigating roads, paths, or walking areas.
Clockwise
Moving in the direction of a clock’s hands. Example: Go around the roundabout clockwise.
Counterclockwise
Moving opposite to a clock’s hands. Example: They ran around the track counterclockwise.
Turn
To change direction. Example: Turn left at the corner and then turn right near the signal.
Curve
A gentle bend in the road or path. Example: Drive slowly on the curve ahead.
Bend
A sharper change in direction. Example: There is a dangerous bend after the hill.
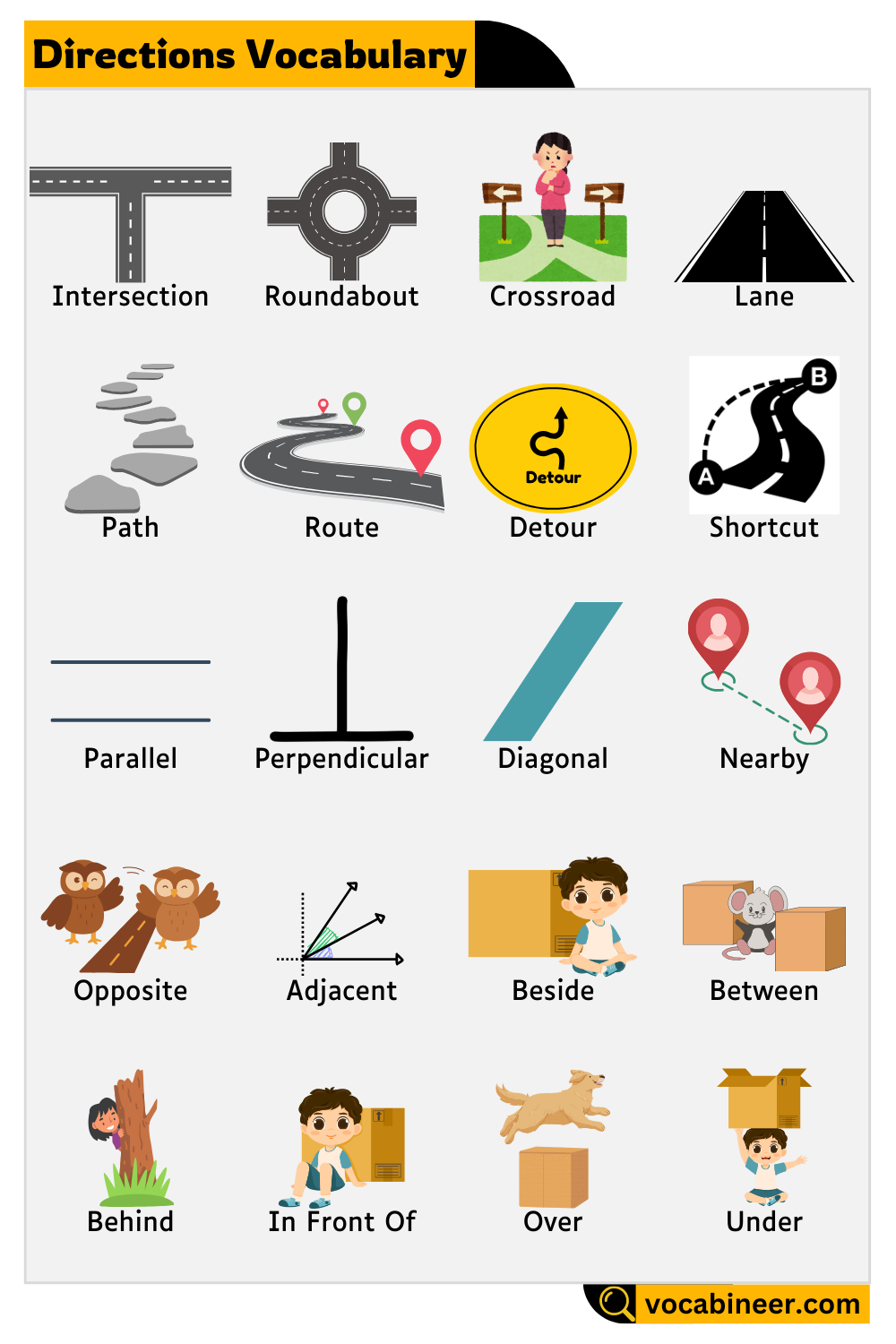
Places and Intersections
These terms are used to describe meeting points or areas in roads, helpful when giving driving or walking directions.
Corner
The meeting point of two roads. Example: Wait at the corner by the pharmacy.
Intersection
Where two or more roads cross. Example: There’s a traffic light at the intersection.
Roundabout
A circular intersection where traffic flows around a center point. Example: Use the second exit on the roundabout.
Crossroad
A place where four roads meet. Example: He lives near the crossroad by the post office.
Lane
A narrow road or a division on a big road. Example: Stay in the left lane to go straight.
Path
A small walkway, often in parks or between buildings. Example: Take the path through the garden.
Route
A planned or regular path from one place to another. Example: This is the shortest route to the bus stop.
Detour
A temporary route used when the main road is blocked. Example: Take the detour around the roadwork area.
Shortcut
A quicker path that saves time. Example: Use the alleyway as a shortcut to school.
Position and Relation
These words describe how one object or person is positioned relative to another. They help create clear spatial descriptions.
Parallel
Lines or paths that run side by side and never meet. Example: The two fences run parallel to each other.
Perpendicular
Lines that form a right angle with each other. Example: The footpath crosses the road at a perpendicular angle.
Diagonal
A line that connects two corners at an angle. Example: Walk diagonally across the park.
Nearby
Close in distance. Example: The store is nearby, just across the street.
Opposite
Directly across from something. Example: The mosque is opposite the hospital.
Adjacent
Located next to or very near. Example: The school is adjacent to the library.
Beside
At the side of something. Example: She sat beside her friend in class.
Between
In the middle of two objects or places. Example: The house is between the park and the shop.
Behind
At the back of something. Example: The car is parked behind the building.
In Front Of
Positioned before or facing something. Example: The kids waited in front of the gate.
Over
Above something, not touching. Example: The plane flew over the city.
Under
Below or beneath something. Example: The cat is hiding under the bed.
Above
At a higher level. Example: The light is above the table.
Below
At a lower level. Example: His shoes are stored below the shelf.
Next To
Immediately beside. Example: The sofa is next to the window.
Near
In close range. Example: A gas station is near the hotel.
Far
At a long distance. Example: The airport is far from the city.
Close
Not far away. Example: The restaurant is close to our office.
Directional Movement
These words show motion or movement patterns in relation to other objects or places. Very useful in navigation and maps.
Along
To move by the side or length of something. Example: Walk along the river to reach the park.
Across
From one side to the other. Example: They walked across the bridge.
Through
In one side and out the other. Example: Drive through the tunnel.
Towards
Moving in the direction of something. Example: He ran towards the exit.
Away From
Moving in the opposite direction. Example: She moved away from the dog.
Inside
Within an enclosed area. Example: The books are inside the bag.
Outside
Not inside; in the open. Example: The kids are playing outside.
Download Directions Vocabulary Infographic PDF
Download your free printable directions vocabulary infographic in high-quality PDF and master location and movement terms with easy-to-remember visuals.
FAQs
1. What are the four main directions in English?
The main directions are North, South, East, and West. These are cardinal directions used on all maps and compasses.
2. What is the difference between clockwise and counterclockwise?
Clockwise follows the direction of a clock’s hands. Counterclockwise moves in the opposite direction.
3. What are position words in directions vocabulary?
They are terms that tell us where something is placed. Examples: under, over, beside, between, behind, in front of.
4. What’s a detour and how is it used?
A detour is a temporary alternative path when the normal road is closed or blocked due to construction or an accident.
5. How can I learn directions vocabulary easily?
Use images, real situations, practice with maps, drawing paths, and speaking them out loud. Group them by categories like movement or location.
6. What’s the use of intercardinal directions like southeast or northwest?
They show specific in-between directions that help describe a more precise location. Useful for navigation apps and detailed maps.
7. Why is directions vocabulary important in English learning?
It improves communication, especially when traveling, giving instructions, or using GPS. It also helps in understanding signs and instructions clearly.