Learning farm animals names is essential for building a strong English vocabulary. Whether you’re a beginner or an intermediate learner, knowing these animals’ names will help you communicate more effectively. In this blog post, we’ll learn the names of common farm animals with their types and categories, helping you improve your vocabulary through pictures. Additionally, understanding the roles of these animals in farming will help in real-world conversations.
Enhance your vocabulary skills with more picture vocabulary on various topics. Visit our Picture Vocabulary section for more.
In This Page
Common Farm Animals
Farm animals play a crucial role in agriculture and daily life. They are raised for various purposes such as milk, meat, labor, and companionship. Below is a categorized list of farm animals with descriptions, helping learners understand their usage and significance in farming.
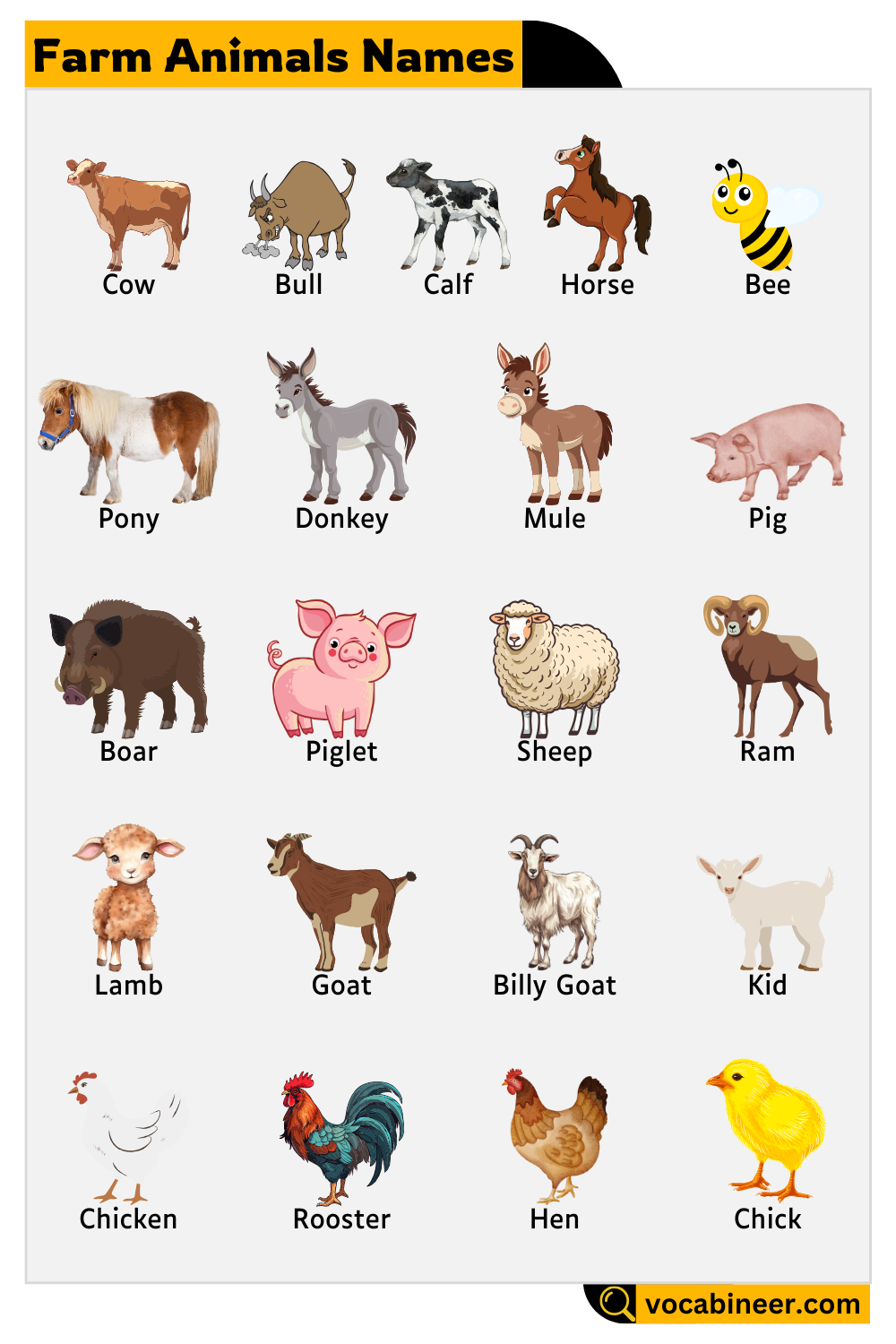
Cattle: Milk and Meat Providers
- Cow – A female cattle known for producing milk, widely used in dairy farming.
- Bull – A strong, male cattle used for breeding, plowing fields, and farm work.
- Calf – A young cattle, either male or female, under a year old, often dependent on milk.
Equines: Work and Transportation Animals
- Horse – A domesticated animal used for riding, pulling carts, and farm labor.
- Pony – A smaller breed of horse, often used for riding by children and herding.
- Donkey – A sturdy animal known for carrying heavy loads in rural areas.
- Mule – A hybrid between a donkey and a horse, stronger than a donkey and commonly used in farming.
Pigs and Related Animals: Meat Production
- Pig – A farm animal raised for pork, requiring proper feeding and care.
- Boar – A wild male pig, sometimes domesticated for breeding.
- Piglet – A baby pig, known for being playful and growing quickly.
Sheep and Goats: Wool, Milk, and Meat Producers
- Sheep – A wool-producing farm animal raised for its fleece and meat.
- Ram – A male sheep, recognized for its curled horns and aggressive behavior.
- Lamb – A young sheep, commonly used to describe tender meat.
- Goat – A farm animal known for producing milk and its ability to climb steep surfaces.
- Billy Goat – A male goat, often distinguished by its long beard.
- Kid – A baby goat, energetic and often raised for dairy farming.
Poultry (Birds Raised on Farms): Egg and Meat Producers
- Chicken – A common farm bird that lays eggs and is raised for meat.
- Rooster – A male chicken that crows loudly and protects hens.
- Hen – A female chicken that lays eggs regularly.
- Chick – A baby chicken, small, fluffy, and dependent on warmth.
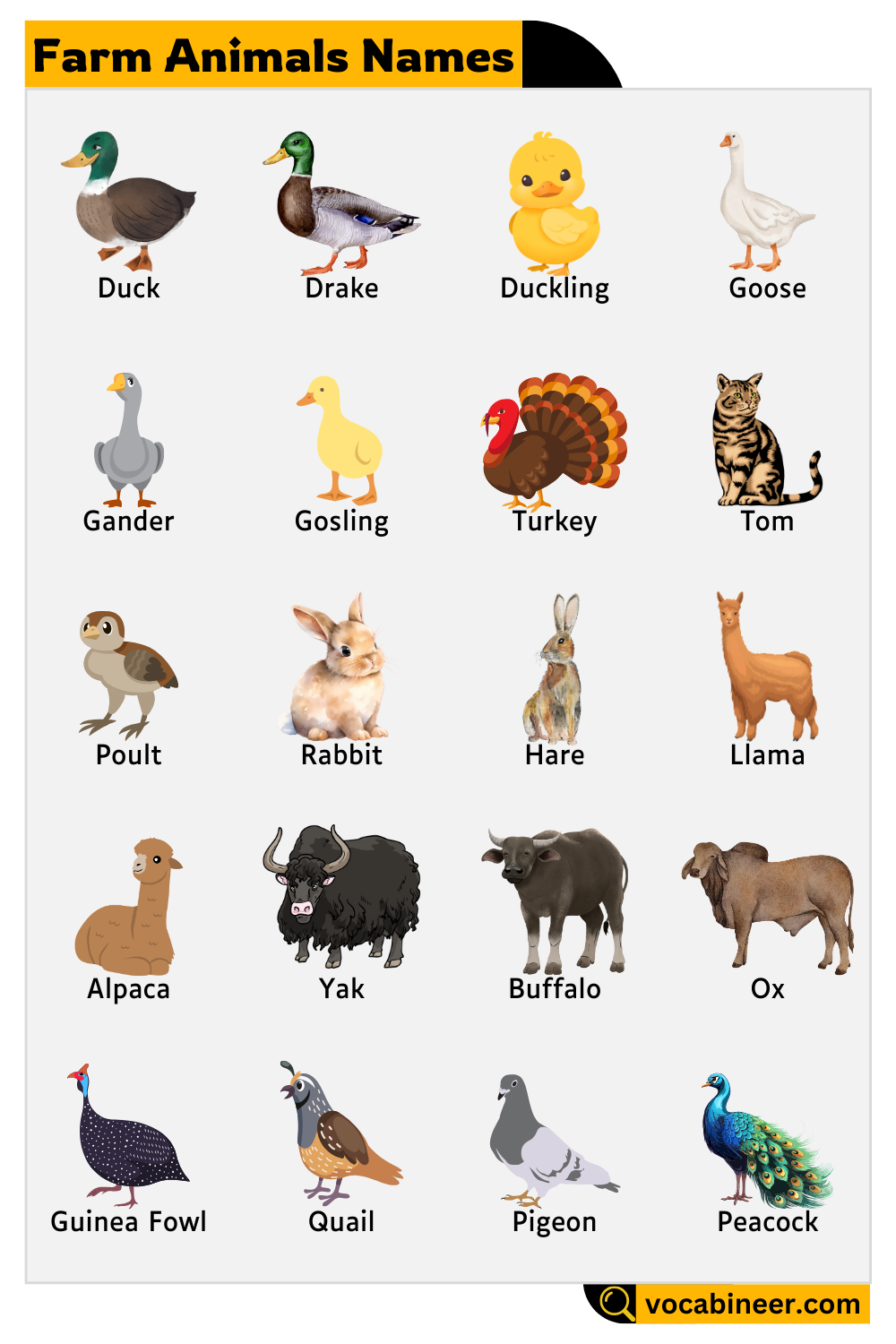
- Duck – A water bird known for its eggs and ability to control pests on farms.
- Drake – A male duck, usually colorful and protective of its flock.
- Duckling – A baby duck, often seen swimming closely with its mother.
- Goose – A large farm bird that lays eggs and provides meat.
- Gander – A male goose, known for its honking and guarding its territory.
- Gosling – A baby goose, fluffy and highly dependent on its mother.
- Turkey – A large bird raised for its meat, especially during holidays.
- Tom – A male turkey, displaying impressive feathers to attract hens.
- Poult – A young turkey, still developing its feathers.
Other Farm Animals: Specialty and Multipurpose Animals
- Rabbit – A small, furry animal raised for meat and fur production.
- Hare – A larger relative of rabbits, known for its speed and long ears.
- Llama – A South American domesticated animal known for carrying heavy loads and producing wool.
- Alpaca – A smaller relative of the llama, valued for its soft wool.
- Yak – A long-haired animal commonly found in mountainous regions.
- Buffalo – A large, powerful animal used for plowing fields and providing milk.
- Ox – A strong male bovine, essential for pulling heavy loads in agriculture.
- Guinea Fowl – A farm bird with spotted feathers, raised for meat and egg production.
- Quail – A small bird kept for its nutritious eggs and meat.
- Pigeon – A farm bird domesticated for meat and messenger purposes.
- Peacock – A striking bird with vibrant feathers, often kept for ornamental purposes.
- Bee – An essential farm insect that produces honey and helps with pollination.
Download Free Farm Animal Infographics
Get high-quality printable farm animal vocabulary infographics in PDF format. Download now to enhance your learning!
FAQs
1. What are the most common farm animals?
The most common farm animals include cows, horses, pigs, chickens, sheep, and goats. These animals are essential for milk, meat, eggs, and farming activities.
2. What is the difference between a goat and a sheep?
Goats are independent, agile, and have straight horns, while sheep are docile, woolly, and usually have curved horns. Additionally, goats tend to browse on shrubs and trees, whereas sheep graze on grass.
3. Why do farm animals have specific names for males, females, and babies?
Different names help distinguish between genders and age groups, which is important for farming, breeding, and animal management. Farmers use these terms to track livestock health and productivity.
4. What farm animals are used for labor?
Animals like horses, oxen, donkeys, and buffalo are commonly used for farm labor due to their strength and endurance. They help with plowing fields and transportation.
5. What is the difference between a rooster and a hen?
A rooster is a male chicken that crows, while a hen is a female chicken that lays eggs. Roosters have more vibrant feathers and a larger comb.
6. Why do farmers keep ducks and geese?
Farmers keep ducks and geese for their eggs, meat, and pest control, as they eat insects and weeds. Additionally, geese act as natural farm guards due to their loud honking.
7. What is the role of bees on a farm?
Bees are essential for pollination, helping plants grow, and they also produce honey. Farms benefit greatly from beekeeping as it increases crop yield.