Learning weather vocabulary in English helps describe daily situations, seasons, and natural changes. Weather words appear in news, conversations, and travel advice. In this blog post, we will learn common weather terms in English with clear categories and pictures to make understanding easy. Knowing these words makes it easier to understand forecasts, describe the weather to others, and follow weather-related warnings or news.
Want to improve your vocabulary with visuals? Visit our Picture Vocabulary section to learn more topics through image-based learning.
In This Page
Weather Vocabulary in English
Weather includes temperature, sky conditions, moisture, and wind. These words help describe what the atmosphere is like at a certain place and time. Learn them to talk about climate, clothes, seasons, and plans. Weather affects how we dress, plan events, and feel throughout the day.
Sun and Light
These words describe different forms and times of sunlight during the day. They are often used in daily conversation, travel, and planning.
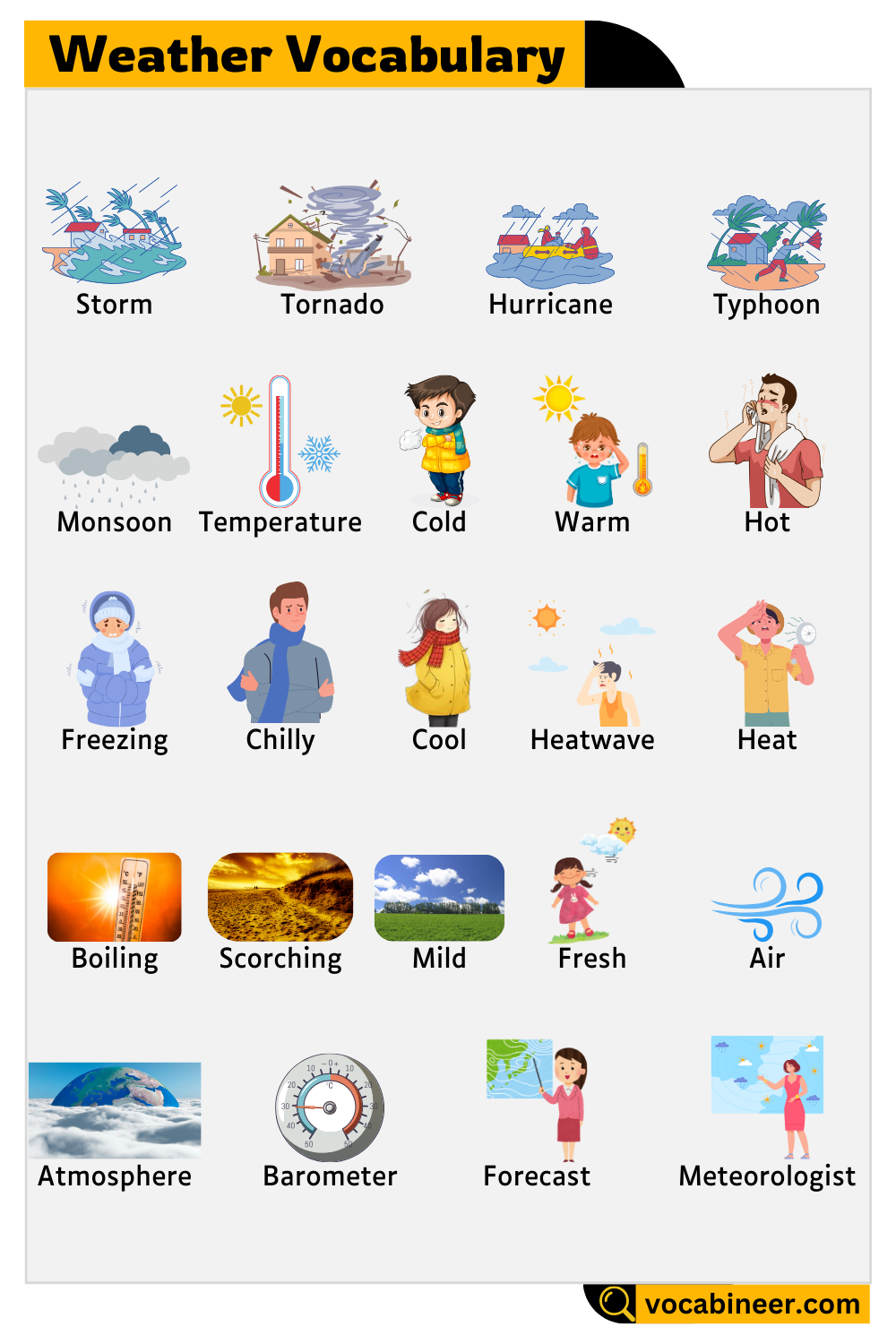
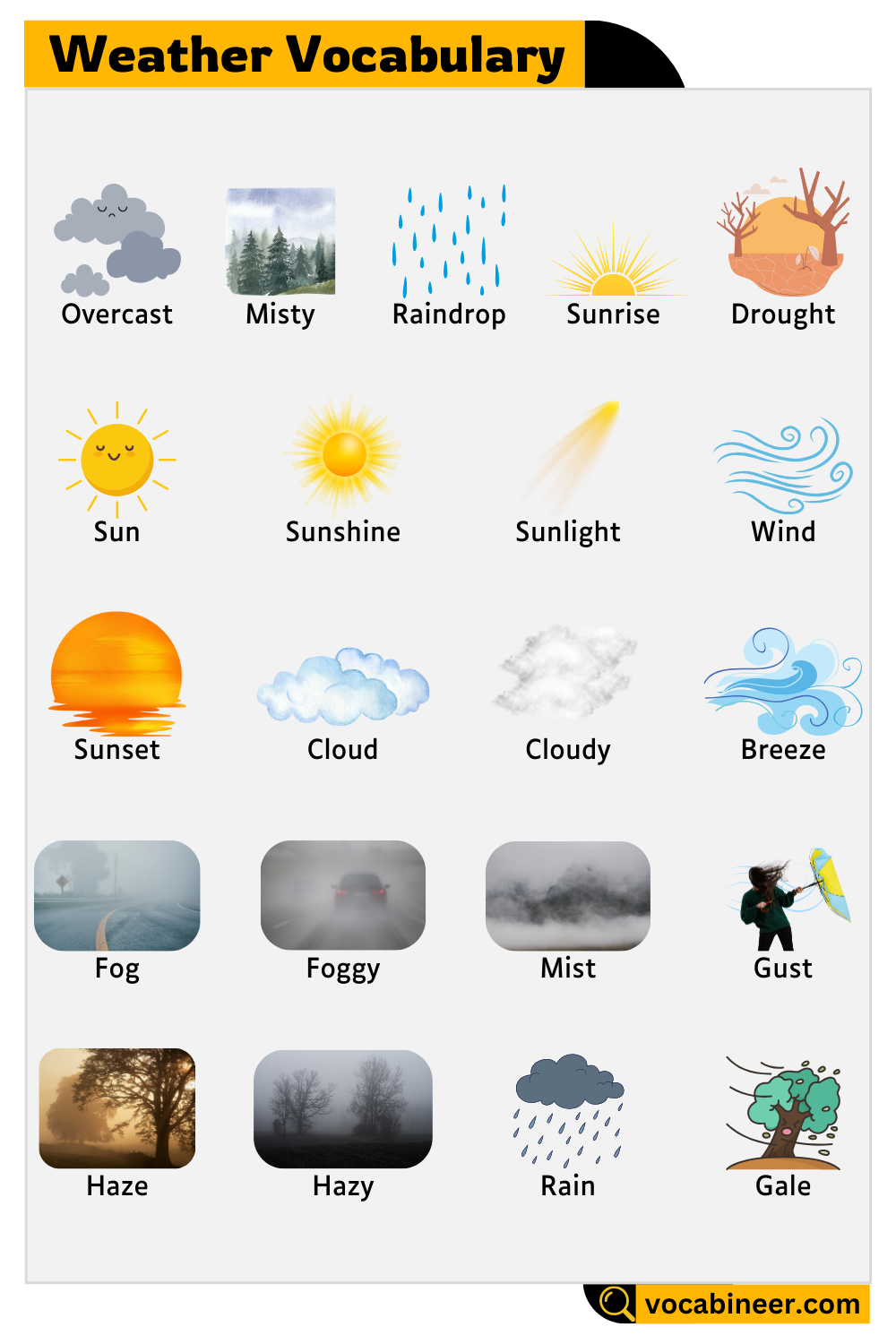
Sun
The bright star that gives us light and heat every day. It rises in the east and sets in the west.
Sunshine
The warm light that comes from the sun. It makes people feel cheerful and gives energy to plants.
Sunlight
Another word for the natural light from the sun. It helps us see during the day.
Sunrise
The time when the sun appears in the morning. It marks the beginning of daylight.
Sunset
The time when the sun disappears in the evening. It signals the end of the day.
Clouds and Visibility
These words relate to what we see in the sky and how clear the view is. These conditions often affect safety while driving or flying.
Cloud
A white or grey shape in the sky made of water droplets. Clouds can bring rain or shade.
Cloudy
When the sky is mostly covered with clouds. It may feel darker outside.
Overcast
A sky that is completely covered by clouds. There is usually no sunshine.
Fog
Thick water vapor near the ground that makes it hard to see. It usually occurs in the early morning or near water.
Foggy
Weather that has a lot of fog and low visibility. Driving becomes more dangerous.
Mist
A light fog that makes the air unclear. It is often seen in valleys or forests.
Misty
A day with mist in the air. It may feel damp and cool.
Haze
A thin cloud of dust or smoke that reduces clarity. It can be caused by pollution.
Hazy
When the air looks blurry or unclear because of haze. It often appears in summer.
Rain and Water
These terms describe rain and water in different forms during rainy weather. Rain affects travel, agriculture, and daily activities.
Rain
Water droplets that fall from clouds. Rain waters plants and fills rivers.
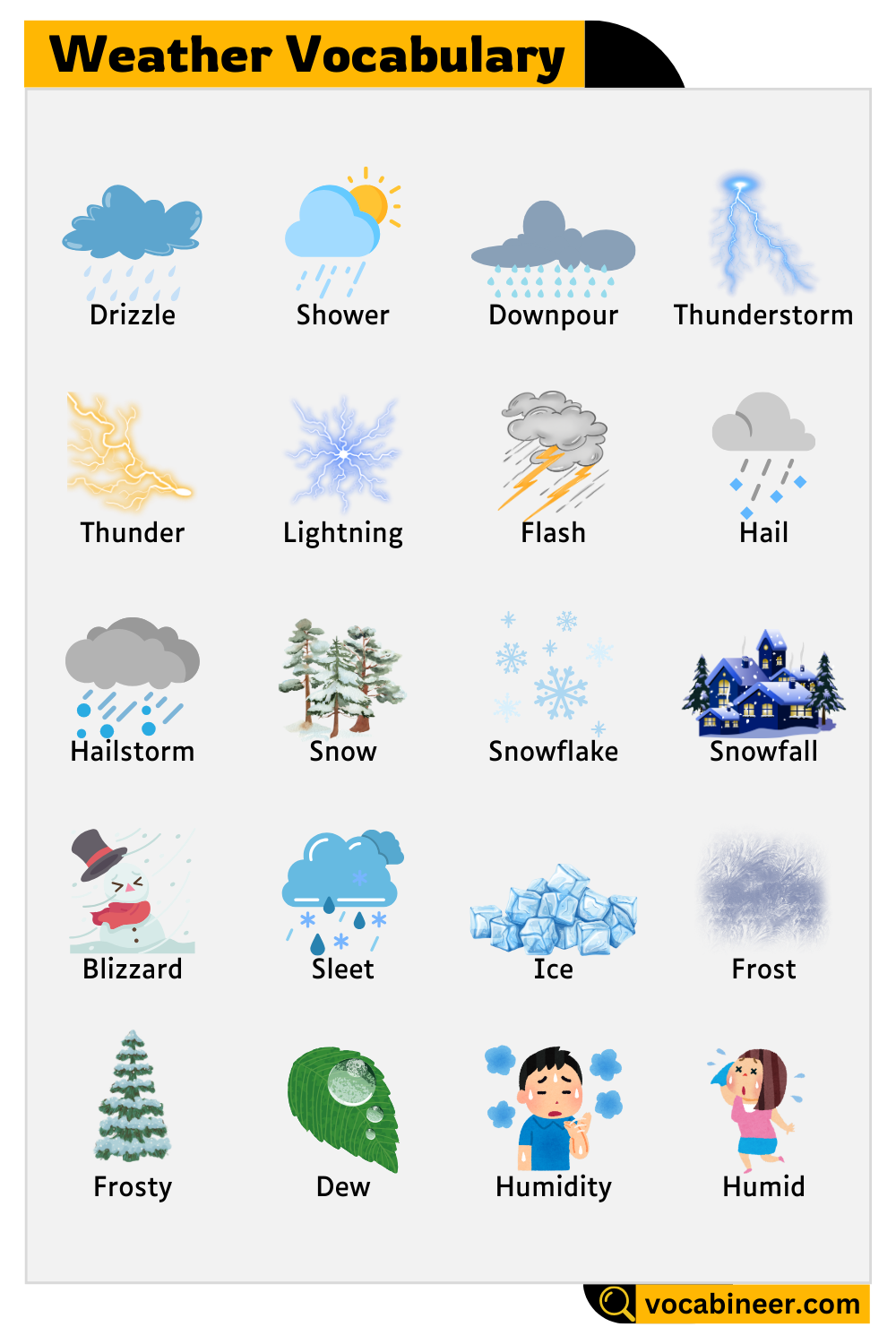
Raindrop
A single drop of rain. Many together make rainfall.
Drizzle
Very light and soft rain. You may not need an umbrella.
Shower
A short period of moderate rain. It usually stops quickly.
Downpour
A very heavy rain that falls fast. It can cause flooding.
Thunderstorm
A storm with thunder, lightning, and heavy rain. It may also bring strong winds.
Thunder
A loud sound that follows lightning. It is caused by air expanding quickly.
Lightning
A bright flash of electricity in the sky. It can be dangerous.
Flash
A quick, bright light in the sky, often from lightning. It lasts only a moment.
Hail
Hard balls of ice that fall during some storms. They can damage cars or crops.
Hailstorm
A storm where hail falls from the sky. It is noisy and sudden.
Snow and Ice
These words are used for cold weather, snow, and frozen conditions. They are common in winter and cold climates.
Snow
Soft white flakes that fall in winter. Children play in it.
Snowflake
A small, unique piece of snow. No two snowflakes are the same.
Snowfall
The amount of snow that falls during a time. Heavy snowfall can stop travel.
Blizzard
A storm with strong wind and heavy snow. Visibility becomes very low.
Sleet
Frozen raindrops that fall like ice. Roads can become slippery.
Ice
Frozen water that forms on surfaces. People must walk carefully on it.
Frost
Thin ice covering grass or windows. It appears on cold mornings.
Frosty
When something is covered with frost. It looks white and shiny.
Dew
Water drops on plants in the early morning. It forms from moisture in the air.
Wind and Air
These terms describe air movement, from soft breezes to strong storms. Wind affects comfort and safety.
Wind
Air that moves from one place to another. It can be soft or strong.
Breeze
A gentle and light wind. It feels nice on a warm day.
Gust
A sudden burst of strong wind. It can blow things away.
Gale
A very strong wind, stronger than a breeze. It can shake trees.
Storm
Severe weather with rain, wind, or snow. It may cause damage.
Cyclone
A rotating storm with strong winds. It happens in coastal areas.
Tornado
A spinning column of air that can cause damage. It looks like a funnel.
Hurricane
A strong storm with wind and rain from the ocean. It affects large areas.
Typhoon
A hurricane in Asia, with high-speed winds. It forms over warm seas.
Monsoon
A seasonal wind that brings heavy rain. It is common in South Asia.
Temperature and Heat
These words describe how hot or cold the weather feels. They help decide what to wear or do.
Temperature
A number that shows how warm or cold the air is. It is measured in °C or °F.
Cold
Air that feels chilly or freezing. You need warm clothes.
Warm
Air that feels pleasant and mild. A sweater is enough.
Hot
When the air feels very warm. You may need a fan.
Freezing
Very cold weather, often below 0°C. Water turns to ice.
Chilly
Slightly cold, needing light clothes. A jacket may help.
Cool
Comfortably low temperature. Often found in spring or autumn.
Heatwave
A period of extreme heat. It may cause health problems.
Heat
The feeling of warmth, often in summer. It may be dry or humid.
Boiling
Very hot, like water at 100°C. It feels uncomfortable.
Scorching
Extremely hot weather, almost burning. Often used in deserts.
Mild
Weather that is neither hot nor cold. It feels easy on the body.
Fresh
Cool air that feels clean and nice. It brings energy.
Other Weather Terms
These are words used in forecasting and weather discussions. They help understand reports and predictions.
Air
The invisible gas we breathe, also part of the weather. It moves as wind.
Atmosphere
The layer of air around the Earth. It contains weather systems.
Barometer
A tool used to measure air pressure. It helps predict weather changes.
Forecast
A report that tells about future weather. It is shown on TV or apps.
Meteorologist
A person who studies and predicts weather. They work at weather stations.
Download Weather Vocabulary Infographic PDF
Get your free printable weather vocabulary infographic in PDF format and learn more through colorful visuals. Visual tools help make memory stronger.
FAQs
1. What are the basic weather vocabulary words in English?
Words like sun, rain, snow, wind, cloud, hot, cold, storm, and fog are common in weather discussions. These terms describe most daily conditions.
2. How can I remember weather terms easily?
Group them into categories like sun, rain, snow, wind, and use pictures for better memory. Practice with flashcards and daily usage.
3. What is the difference between mist and fog?
Fog is thicker and reduces visibility more than mist. Mist is lighter and often appears in the morning. Both form from water droplets.
4. What’s the difference between hurricane and typhoon?
They are the same type of storm. A hurricane happens in the Atlantic, while a typhoon happens in the Pacific. Both have strong winds and rain.
5. Who gives us weather information?
A meteorologist studies the weather and gives the forecast using tools like a barometer. They share information through news and websites.
6. What is a heatwave?
It’s a period of very high temperatures for several days that can be dangerous for health. People should drink water and stay indoors.
7. Why should English learners study weather vocabulary?
Weather terms are used in everyday talk, news, and travel plans, so learning them improves real-life English. It also helps with reading signs and apps.